In this article Dr Bob Struijk, vice-president of FANUC Europe, discusses how robotics, once primarily the domain of automotive manufacturing and assembly, has increasingly made inroads into the production of aircraft. Aerospace Manufacturing hears more.
Since our inception in 1956, FANUC has been a pioneer in the development of numerically controlled machines and automation in manufacturing. Now the FANUC Corporation is one of the worldwide leaders in factory automation with our widely used CNC control systems, robots, and production machinery, including RoboDrill, RoboCut and RoboShot. We operate from 271 locations worldwide with a comprehensive network of sales, technical support, R&D, logistics and customer service, employing more than 8,000 people.
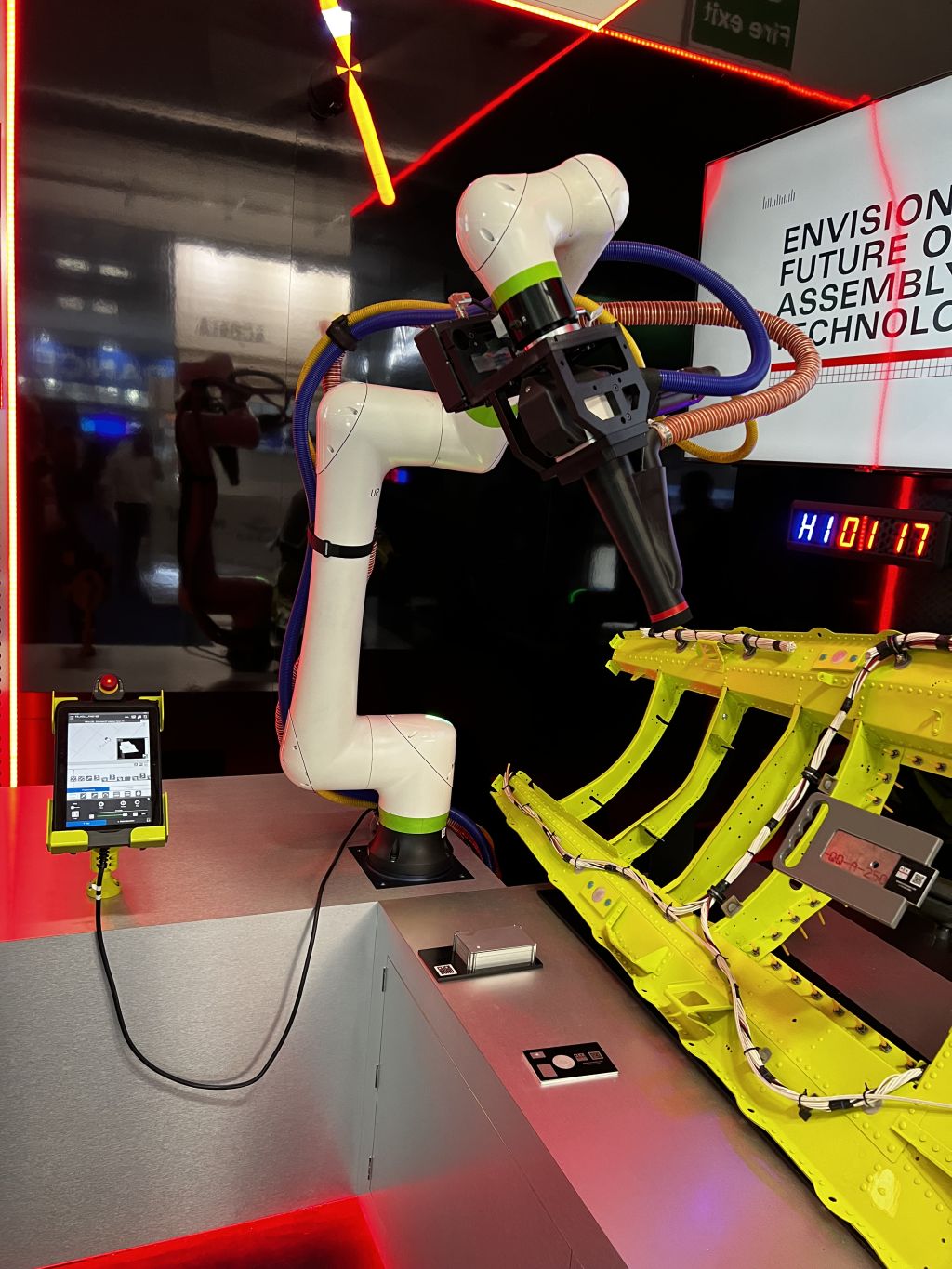
In recent years, the aerospace manufacturing sector has seen remarkable advancements thanks to the integration of automation with robotics. As the technology continues to evolve, industrial robots have become indispensable in streamlining processes, increasing productivity, ensuring precision and enhancing overall safety in the aerospace industry. And FANUC has been at the forefront of developing various robot applications for aerospace manufacturing with the aim of making a significant contribution to this critical sector.
Precision and accuracy
In aerospace manufacturing, precision and accuracy are paramount. Even the slightest deviation in a drilling head alignment or rivet assembly can have severe consequences. For this reason, we have introduced robots with secondary encoders to ensure superior precision and repeatability, helping to play a crucial role in achieving the highest quality standards required by the industry.
These robots can handle complex tasks with ease and deliver consistent results for long periods, minimising errors and rework. Originally, only high payloads of up to 700kg were possible with our robotic systems, but we have since developed compact models for payloads of 60kg and 190kg. These are ideal for use on movable platforms or for positioning in tight spots on an assembly line. Additionally, robotic arms equipped with advanced sensors and vision systems can also enable efficient assembly of intricate components and facilitate the integration of delicate parts.
Moreover, unlike human employees, robots can work tirelessly around the clock, eliminating the need for breaks or shift changes and improving overall production efficiency. And the introduction of lightweight collaborative robots (cobots), such as the FANUC IP67-rated CRX range, has proved to be a gamechanger; able to be used safely around and next to employees, cobots allow for collaboration on the shopfloor and can speed up valuable process time.
Composite fibre fixes
As the aerospace industry has witnessed a shift towards the use of lightweight composite materials due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, there has been a need to develop more automated manufacturing techniques with these materials, however, working with composites demands specialised techniques and expertise. Fortunately, robots are well-suited to handle this challenge.
Automated fibre placement and automated tape laying are two vital processes in composite manufacturing and FANUC’s CNC controls are capable of controlling the multiple axes in large fibre lay-up machines, while we also apply our servo motors as an external axis, controlled directly by the FANUC robot.
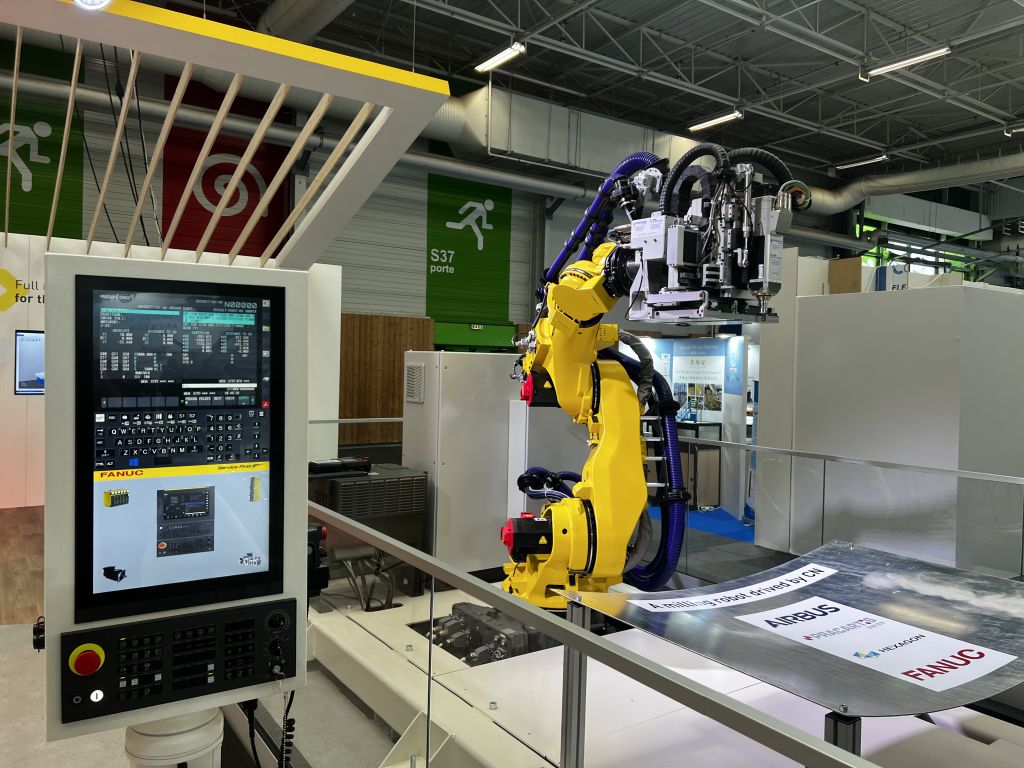

Robots equipped with these capabilities can position carbon fibres and prepreg tapes with extraordinary precision, producing composite components that meet the highest quality standards. Furthermore, their superior levels of precision and accuracy mean that robots reduce waste and material costs, making the manufacturing process more sustainable.
Supplementing safety
Aerospace manufacturing often involves hazardous tasks, such as working with heavy materials, in extreme temperatures, or in confined spaces. Delegating dangerous tasks to cobots and robots significantly enhances worker safety.
Added to this, robots can be employed in inspection and maintenance tasks, enabling the assessment of difficult-to-reach areas, and avoiding potential hazards for human workers. For example, iRvision is FANUC’s proprietary vision system that can be used for tasks such as on-the-fly inspection of parts and detection of faulty assemblies. By minimising human intervention in hazardous operations such as these, aerospace manufacturers can protect their workforce and focus on producing high-quality products.
Lastly, the assembly of aerospace components demands a high level of precision and synchronisation. Robots can perform complex assembly tasks with multiple degrees of freedom, ensuring seamless integration of components. Able to follow programmed paths, they can carry out consistent and reliable assembly procedures, eliminating variations in the final product.
A driving force
Robotic automation has become a driving force in advancing the aerospace manufacturing sector. From improving efficiency and precision to enhancing safety and enabling agile manufacturing, robots have revolutionised the way aerospace components are designed, manufactured, and tested.
And given the backlog in orders in the aerospace industry, made worse by the pandemic, the time gained in throughput by using flexible robot automation is another key benefit. As technology continues to progress, we can expect ever more sophisticated robotic systems with enhanced AI capabilities, which will further elevate the productivity and quality of aerospace manufacturing.
Embracing automation and robotics in the aerospace industry is not simply a trend; it is a necessary step towards achieving greater heights in innovation and reliability in this critical sector.
www.fanuc.eu